FAEE Hair Test: Definition, Purpose, and Accuracy
10 October, 2023

The FAEE hair test, or Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters (FAEE) test, is a non-invasive method of detection of alcohol use and misuse. It detects a type of metabolite that is formed when alcohol is consumed. The hair test is commonly used in healthcare settings where monitoring of alcohol abstinence is important. It is a highly accurate method of testing as the hair specimen is stable and does not degrade over time.
The hair stores alcohol metabolites as they enter the follicle after the breakdown of alcohol compounds. FAEE and EtG (Ethyl Glucuronide) are some of the byproducts of ethanol, the substance found in alcoholic beverages. Therefore, their presence indicates alcohol consumption. The hair test is a reliable way to determine chronic alcohol use or disorder. In this article, we will focus on the process of FAEE testing, its purpose, and its accuracy.
What is the FAEE Hair Test
The FAEE hair test is a method for detecting excessive alcohol consumption over a period of time. It traces fatty acid ethyl ester concentrations in hair, which can only be produced if a person consumes alcohol. Unlike other test methods, hair alcohol testing can trace substances for the past three months, and FAEE tests can be longer for up to ten months. This is because the alcohol markers deposit in the hair strands as they grow.
The hair test provides several advantages over other alcohol testing methods. Primarily, its long detection window allows for a more comprehensive assessment of an individual’s alcohol consumption habits. By analysing a small sample of hair, the test can determine the pattern of alcohol use over time. Additionally, it is a non-invasive and relatively simple sample collection process.
It is important to note that the test does not measure current intoxication levels but rather provides evidence of past use. For determining current impairments, a breath test is more suitable. A breathalyser device measures the blood alcohol levels and gives the results in seconds. Other methods include the EtG tests in urine or blood.
Reasons to Test
- Determine a person’s long-term behaviour by looking at an overview of up to ten months of alcohol consumption patterns.
- Detect alcohol biomarkers for an extended time period.
- Assess whether someone has violated a sobriety or alcohol-related policy.
- Provide evidence in legal cases, such as driving under the influence (DUI) charges, probation, or child custody cases.
- Provide healthcare professionals with an accurate assessment of a patient’s condition to develop appropriate treatment plans.
- Monitor individuals in alcohol rehabilitation programs.
- Assess the alcohol consumption habits of prospective employees in a safety-critical role.
- In some cases, random monitoring in the workplace to identify employees with potential chronic alcohol abuse.

Purpose of the FAEE Hair Test
The purpose of the FAEE hair test is to detect alcohol biomarkers for a comprehensive analysis. The presence of FAEE metabolite in the hair is a good indicator of excessive alcohol consumption. Moreover, its long detection window is ideal for the diagnosis of alcohol abuse as well as the monitoring of alcohol abstinence. For example, health professionals can check if a patient has a relapse.
Another important use of hair alcohol testing is for forensic purposes and legal cases. The test can support or refute claims of alcohol consumption in drink driving, child custody, and workplace incidents. Additionally, this test can provide a more accurate and reliable assessment of a person’s alcohol behaviour compared to self-reported screening tests, which can be biased.
Hair testing can be used in conjunction with other assessment tools to guide effective treatment plans and interventions. Healthcare professionals can also use the test to develop an integrated approach to help individuals manage their alcohol consumption. Overall, it serves as a valuable monitoring tool for long-term excessive consumption patterns and provides objective evidence in various contexts.
Procedure
The process of hair testing is simple. It involves collecting a sample of hair from the individual, usually taken from the scalp. The length of hair required varies depending on the testing facility. Generally, approximately 5cm length is ideal to get three months’ worth of data.
If head hair is not available, body hair is a suitable alternative. However, the length may differ as the growth rate of hair in the body is slower. Next, the sample is sent to a laboratory for testing. In the laboratory, technicians wash the hair to remove any external contaminants.
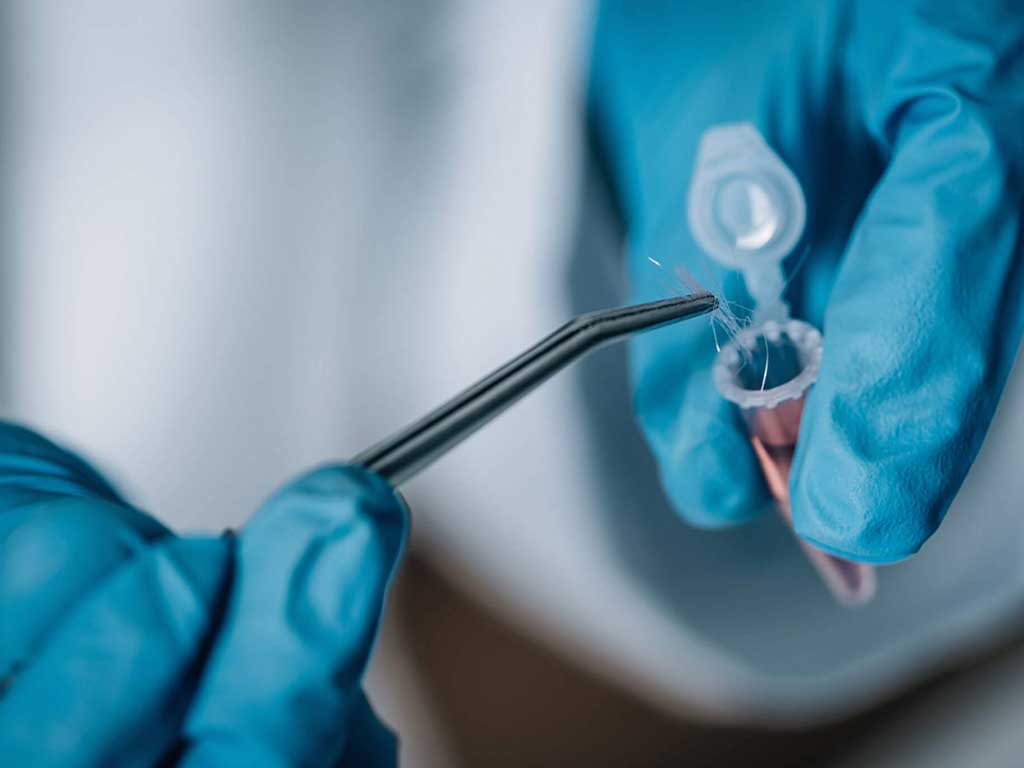
Accuracy and Reliability of the FAEE Hair Test
The FAEE hair test is considered to be a reliable indicator of chronic excessive alcohol consumption. It has a high accuracy rate as it measures the direct biomarkers of ethanol. Furthermore, the hair analysis uses gas chromatography/liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. The GC-MS test is the “gold standard” in substance identification. Laboratories establish cut-off levels to distinguish between low and heavy alcohol use.
The test uses four FAEE markers, including ethyl myristate, ethyl palmitate, ethyl oleate and ethyl stearate. These metabolites of ethanol can provide a reliable estimate of drinking patterns. They deposit durably via blood vessels into the hair shaft. Thus, it is difficult for individuals to manipulate the results by simply abstaining for a few days.
However, there is a risk of false negatives if an individual uses adulterants like detox shampoos. Studies show that detox shampoos have the potential to alter alcohol concentrations in hair and have a great wash-out effect. As such, laboratories will screen the sample for adulterants or contamination to ensure accuracy.
Risks of False Positives
There are limitations to hair testing that may risk false positives. The FAEE test is susceptible to hair products containing alcohol. Additionally, some may naturally have higher levels of FAEE even if they did not consume alcohol, leading to false-positive results.
Subsequently, substance abuse professionals recommend combining FAEE and EtG analysis to balance out their strengths and weaknesses. These two tests can provide a comprehensive overview of a person’s consumption of alcohol over a period of time. Laboratories may render the test invalid if the hair sample has extensive chemical treatments. They may suggest using body hair samples or nails.
Conclusion
The FAEE hair test is a reliable and accurate assessment of long-term or chronic excessive alcohol consumption. It detects fatty acid ethyl ester or FAEE, which is a specific metabolite of alcohol produced in the blood. These metabolites enter the hair follicle and deposit in the hair as it grows. As a result, it is detectable in the hair for three months or longer. Moreover, this test can provide valuable information for healthcare professionals monitoring a person’s abstinence.
It is important to follow the guidelines for hair alcohol tests as instructed by a professional or the testing kit. The results are usually available after a few days, indicating positive or negative results. However, it is crucial to interpret the results with caution, as the test cannot determine the quantity of alcohol consumption. External factors can also influence the results. Thus, preventive measures are in place to minimise the risk of overestimation or false positives.