Alcohol and Urine: Effects, Detection, & Factors Affecting Alcohol Concentration
17 April, 2024

Alcohol consumption is a common part of social gatherings and celebrations. It is well known that alcohol affects various body systems, yet many people are curious about the relationship between alcohol and urine. Alcohol can cause concentrated urine, which can irritate the bladder lining. In addition, alcohol is detectable in urine within an hour of consumption and up to 24 hours after the last intake. The concentration levels may depend on number of drinks, weight, and liver function.
Heavy drinking can cause severe impairment, affecting judgment, perception, memory, reaction time, and coordination. Hence, it is a high risk of accidents, injuries, and health problems. In the workplace, it can lead to lead to endanger other employees and lead to high medical expenses and low productivity. Therefore, various settings implement alcohol testing programs to minimise these risks. This article will explore the effects of alcohol on urine, urine testing, and factors that can influence alcohol concentration.
Effects of Alcohol on Urine
Alcohol is a diuretic, which means it causes the body to lose fluids. It can produce urine flow within 20 minutes after consumption. Alcohol does this by inhibiting the production of vasopressin, an antidiuretic hormone. This causes the kidneys to reabsorb water. Without vasopressin, the bladder fills up with urine, causing frequent urination.
Moreover, concentrated urine can irritate the bladder lining and contribute to discomfort or inflammation. It can also increase urine acidity and the risk of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI). Another effect of alcohol on urine is changes in colour and odour. Dark urine is a sign that the body is not getting enough fluids and can be a warning sign to increase water intake.
Finally, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to the presence of byproducts in urine that are not normally found. These can include acetaldehyde and acetone. The presence of these substances can potentially damage the liver and other organs. Therefore, monitoring urine changes and seeking medical advice if necessary, can help in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Understanding Alcohol Metabolism in the Body
- When alcohol is ingested, it is absorbed into the bloodstream and then processed by enzymes in the liver.
- The liver breaks down alcohol into acetaldehyde, a toxic substance that can cause cell damage if not further metabolised.
- The liver can process one standard drink per hour.
- Acetaldehyde is then converted into acetate, which is eventually broken down into carbon dioxide and water and eliminated from the body.
- Individuals with a slower metabolism may have a higher concentration of alcohol even after a longer period.
- The more a person drinks, the longer time it takes for it to exit the system completely.
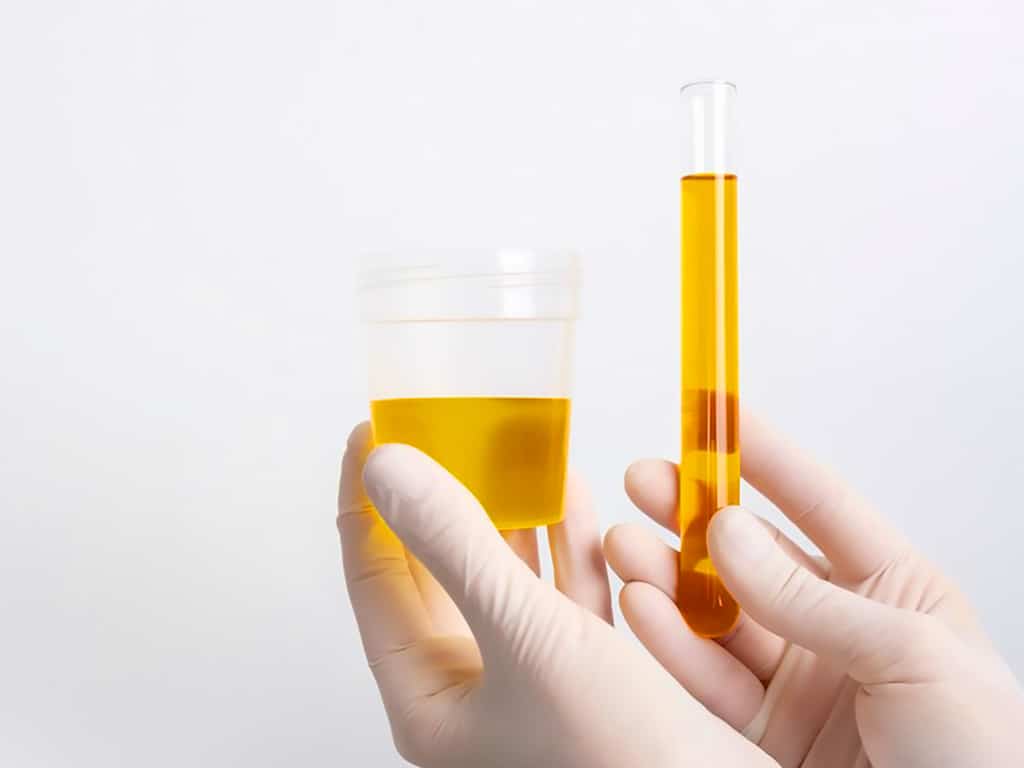
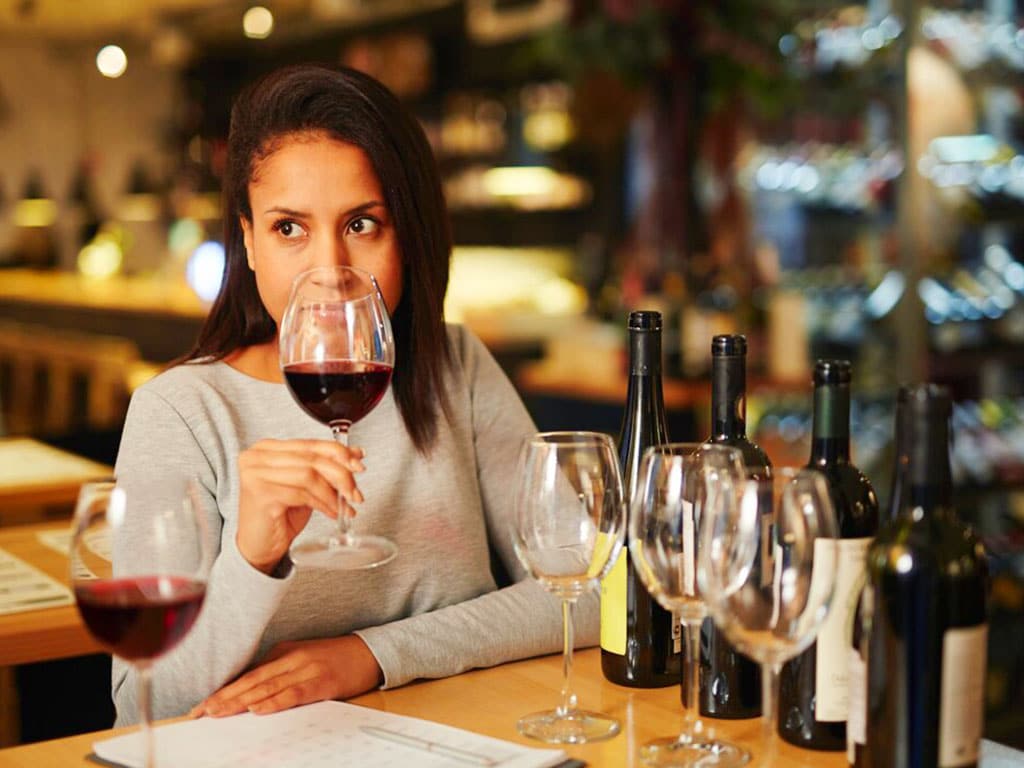
Alcohol and Urine – Detecting Alcohol Use Through Urine Samples
A common method to detect alcohol use is through urine tests. It is the process of examining the urine samples for the presence of ethanol or its metabolites. The test is preferred by many workplaces and clinical settings because it is easy to administer and provides quick results. It can also help assess if a person has an alcohol use disorder or has problematic drinking patterns.
There are two main types of alcohol detection tests. The first type is alcohol screening. In this method, the person provides a urine sample and immerses it into a testing device containing immunoassays. This causes a reaction that produces a colour change if ethanol is present. However, it does not measure the concentrations of alcohol in urine.
The second type is Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). It is a more sophisticated and sensitive technique that requires laboratory analysis. This method can detect even trace amounts of ethanol, providing a more accurate measurement of blood alcohol content. Furthermore, it can distinguish between different metabolites, such as Ethyl Glucuronide (EtG) and Ethyl Sulfate (EtS).
Accuracy and Reliability of Urine Tests
Urine tests are generally reliable and accurate, being the most researched procedure. In particular, GC-MS is considered the gold standard in alcohol testing. It can identify specific substances with high specificity. Thus, this method often serves as confirmatory testing for initial screening with non-negative results.
On the other hand, immunoassay tests are less reliable due to the possibility of false positives or false negatives. This can be due to external factors that may interfere with the test. In addition, there are limitations to consider. For instance, it is not an accurate indicator of intoxication levels due to its extended detection times.

Alcohol and Urine – Factors Affecting Alcohol Concentration in Urine
Several factors can influence the concentration of alcohol in urine. The foremost factor is the frequency and amount of alcohol. When ethanol or metabolites reach the cut-off level of the screening kits, it produces a non-negative result. It indicates detecting a significant concentration level of alcohol. Moreover, large doses increase the symptoms of intoxication. Regular consumption also leads to a more extended period of detection.
The time since the last drink is also a crucial factor in alcohol urine tests. The concentration of alcohol is highest within a few hours of consuming alcoholic beverages. As time passes and the body eliminates the compounds, the concentration in urine decreases. Therefore, the timing of the urine test is important in determining its accuracy.
Furthermore, individual factors play a huge role in the urine alcohol content. These include hydration levels, metabolism rate, and medication interactions. Drinking plenty of water can dilute the urine, reducing the concentration of alcohol. Likewise, the rate at which the individual metabolises ethanol can vary. Lastly, prescription drugs like diabetes and anti-anxiety medications are known to interact with alcohol and increase their effects.
Detection Window
In general, the detection window of alcohol is between 24-48 hours in urine. The liver processes alcohol at a constant rate of one standard drink per hour. This window can be shorter for light-drinking individuals. Conversely, chronic heavy drinkers have a longer detection time of up to 72-80 hours or more in EtG tests.
It is also important to note that the detection period in urine is different from blood tests, saliva tests, and hair follicle testing. Blood and saliva tests have shorter detection windows, while hair tests can trace alcohol for up to 90 days.
Conclusion
Understanding the effects of alcohol on urine can help individuals make informed decisions about their drinking habits. Alcohol is a volatile substance that is rapidly metabolised in the body. Excessive drinking often leads to severe impairment. This increases the risk of road or workplace accidents and injuries. Additionally, changes in urine colour, frequency, or odour, may indicate underlying health issues. This may include liver failure, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Urine testing is one of the efficient methods to detect alcohol use. It involves collecting urine and analysing it through various techniques. Urine tests can detect ethanol metabolites for up to three days. Moreover, it is vital to be aware of the factors that can affect alcohol concentration in urine. This includes metabolism rate, hydration levels, and medication interactions. In conclusion, alcohol is detectable in urine, but the concentration and detection window can vary on several factors.