Drug and Alcohol Test: A Complete Guide for Workplace Testing in NZ
07 February, 2024

Drug and alcohol tests in the workplace have become an essential aspect of maintaining a safe and productive work environment. As businesses strive to ensure the well-being of their employees, implementing testing programs has become crucial. These tests identify individuals who may be under the influence of illicit drugs. Thus, positive results can have serious implications. It is essential for companies to follow strict procedures to avoid legal issues and ensure fairness in the testing process.
Alcohol and illegal drug use is a major hazard in the workplace. It impairs the physical and mental abilities of a person, especially when performing tasks that require alertness and attention. Additionally, long-term use can cause serious health issues, including substance use disorder. Therefore, organisations implement drug and alcohol policies to combat these hazards. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a complete understanding of the importance of workplace testing, the different types of tests, and implementation procedures.
Jump to a Section:
- An Overview of Drug and Alcohol Tests in New Zealand
- Importance of Conducting Drug and Alcohol Tests in NZ Workplaces
- Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Breathalysers
- Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Urine Tests
- Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Blood Tests
- Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Hair Tests
- Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Saliva Tests
- Drug and Alcohol Test Methods and Techniques
- Implementing Drug and Alcohol Tests in NZ
- Drug and Alcohol Test Training
An Overview of Drug and Alcohol Tests in New Zealand
Drug and alcohol tests in New Zealand are becoming increasingly common as employers recognise the importance of ensuring a safe workplace. The country has specific laws and guidelines that govern workplace testing to maintain a substance-free environment. At the same time, it is essential to protect the rights and privacy of employees while carrying out these tests.
The Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 requires employers to provide a safe working environment for employees. This includes managing the risks associated with drug and alcohol use. This act also allows employers to conduct testing if they have a reasonable cause to believe that workers are impaired. However, establishing clear policies is important to facilitate these measures.
The consequences of positive test results can vary depending on the industry and the company policies. In safety-sensitive industries like mining or construction, it may lead to immediate suspension, termination, or mandatory rehabilitation programs. Overall, drug and alcohol monitoring in the workplace is crucial for maintaining a safe and productive environment for employees.
A Brief History
- Workplace testing was introduced in New Zealand in the early 1990s as a response to USA International Companies adopting policies and procedures.
- In 1992, the NZ Navy introduced drug testing programs, and other Armed Forces soon followed.
- Since 2000, the high-risk sectors have organisations mandating alcohol and drug testing.
- Initially, testing was conducted through observation and physical symptoms. Later on, it evolved to include more sophisticated methods, such as urine and saliva testing.
- In 2001, The Australia/New Zealand (AS/NZ) Standards were established to provide guidelines for workplace testing and occupational health and safety. These standards ensure that the tests are accurate, reliable, and fair.

Importance of Conducting Drug and Alcohol Tests in NZ Workplaces
Conducting drug and alcohol tests in NZ workplaces is of utmost importance for several reasons. Firstly, ensuring a safe and healthy environment is crucial for both the employees and the employer. Drug and alcohol use can impair judgment, coordination, and concentration, leading to an increased risk of accidents and injuries. Thus, workplace testing identifies at-risk workers, allowing employers to take appropriate measures.
Secondly, workplace drug and alcohol screening can contribute to the overall performance and productivity of a company. Substance abuse can lead to negative outcomes, such as decreased work quality, absenteeism, increased errors, and conflicts among employees. By ensuring a drug and alcohol-free workplace, organisations can diminish these negative impacts.
Thirdly, workplace testing in NZ is essential for legal and regulatory compliance. This is particularly important in safety-sensitive industries where the risks associated with substance use are higher. Employers have a duty of care to their employees to take practicable steps to maintain a safe working environment. Non-compliance with these laws can lead to legal consequences and financial penalties.
Benefits of a Safe Working Environment
Maintaining a safe working environment through alcohol and drug testing offers numerous benefits. The foremost benefit is the reduced risk of accidents. When employees are clean and sober, they are less likely to make errors or engage in risky behaviour. This not only prevents injuries but also minimises the number of sick days.
Another benefit is enhanced productivity and efficiency. When employees feel safe, they are more likely to perform at their best. This leads to increased job satisfaction, employee morale, and company reputation. By identifying substance abuse issues, employers can seek treatment and support, ultimately improving employee well-being and reducing turnover rates.

Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Breathalysers
A common in a workplace drug and alcohol test is using a breathalyser. It is a device that measures Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) by analysing the exhaled breath. Breathalysers contain powerful sensors that can detect alcohol molecules. The sensors chemically react with the alcohol and produce an electrical current.
The magnitude of the electrical current corresponds to the amount of alcohol in the breath, in proportion to the alcohol in the blood. This output is then measured by the device and converted into the BAC level. Hence, it provides reliable information about the intoxication or impairment degree of a person.
There are different types of breathalysers available, including handheld devices used in roadside screening and larger equipment in police stations. Individuals can also get one for personal use. It is a non-invasive procedure and provides quick results after a few seconds after sample collection. Moreover, this method does not require laboratory analysis, making it a convenient and cost-effective option for alcohol testing.
Accuracy of Breathalyser Tests
Breathalysers are generally reliable in detecting alcohol use. The accuracy can vary depending on various factors. Primarily, breathalysers use two types of sensors: semiconductor and fuel cell technology. Semiconductor sensors are less expensive but can be sensitive to other substances. Meanwhile, fuel cell sensors are less prone to interference, providing more accurate results.
Furthermore, the accuracy of the breathalyser includes recalibration, user error, and external factors. Periodic recalibration is vital to maintain the performance of the sensors. On the other hand, not following proper breath testing procedures, improper handling of the device, and mouth alcohol can affect the results.
Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Urine Tests
Urine analysis is another standard in drug and alcohol tests in workplaces. Urine testing is an efficient method of detecting a wide range of substances. It includes alcohol, illegal drugs, and prescription drugs. The test involves collecting a urine sample from the individual and analysing it using various techniques. It can provide valuable information about drug and alcohol use within a certain period.
A common method of analysis is the immunoassay testing. It works by using antibodies to detect alcohol or drug metabolites in the urine specimen. If the initial test indicates the presence of a target substance, confirmatory testing using a more accurate technology, such as Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS), is crucial.
Urine drug testing can detect substances such as marijuana, cocaine, opioids (heroin, morphine), amphetamines, and benzodiazepines. It can also identify prescription medications that may be abused. These substances are detectable in urine for varying periods, depending on the specific drug and amount of consumption. Typically, drugs stay in urine for one to three days up to a week.
Advantages of Urine Tests
- Urine testing is easy to administer. The sample collection procedure is less invasive and provides immediate results, ranging from a few minutes to hours.
- The detection window of drugs in urine samples is longer in contrast to blood or oral fluids.
- It is a cost-efficient method of drug testing. The test kits are affordable and easily accessible in pharmacies or online.
- Urine test kits are easy to use. Individuals can get reliable results following the instructions provided in the kit.
- Urine specimens allow retesting. The samples can be forwarded to a laboratory for confirmation if the initial screening shows a non-negative result.
Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Blood Tests
Blood analysis is one type of drug and alcohol test method that can provide the most accurate result. Unlike urine tests, which detect metabolites, blood tests directly measure the presence of substances in the bloodstream. Additionally, drugs stay in the blood for a shorter period, usually within 6-12 hours. Therefore, the results of the test indicate real-time updates, making it highly reliable for recent use or current impairment.
To conduct a blood test, a healthcare professional will draw a small sample of blood from the individual. This sample is secured and is then sent to an accredited laboratory for analysis. They can identify the specific substance and its precise concentration level.
However, the process of analysis is more complex, resulting in a longer turnaround time. The sample collection procedure can also be intrusive for some people. Nevertheless, its high accuracy rate makes it admissible in court or legal proceedings. Overall, blood tests provide valuable information about the recent substance use of a person, which can be a factor in accidents.
When to Use Blood Tests
Blood tests are valuable in situations where the detection of recent drug or alcohol use or current impairment is crucial. One common situation is post-accidents. Since blood analysis provides real-time updates, it can determine if recent substance use is a contributing factor to the incident.
Furthermore, it is often used as confirmatory testing when initial urine or oral fluid tests show a positive result. It can measure the precise levels of substances that may not be available with immunoassay techniques. Moreover, blood tests can also be used for medical purposes, such as monitoring drug levels in patients undergoing medication treatment.
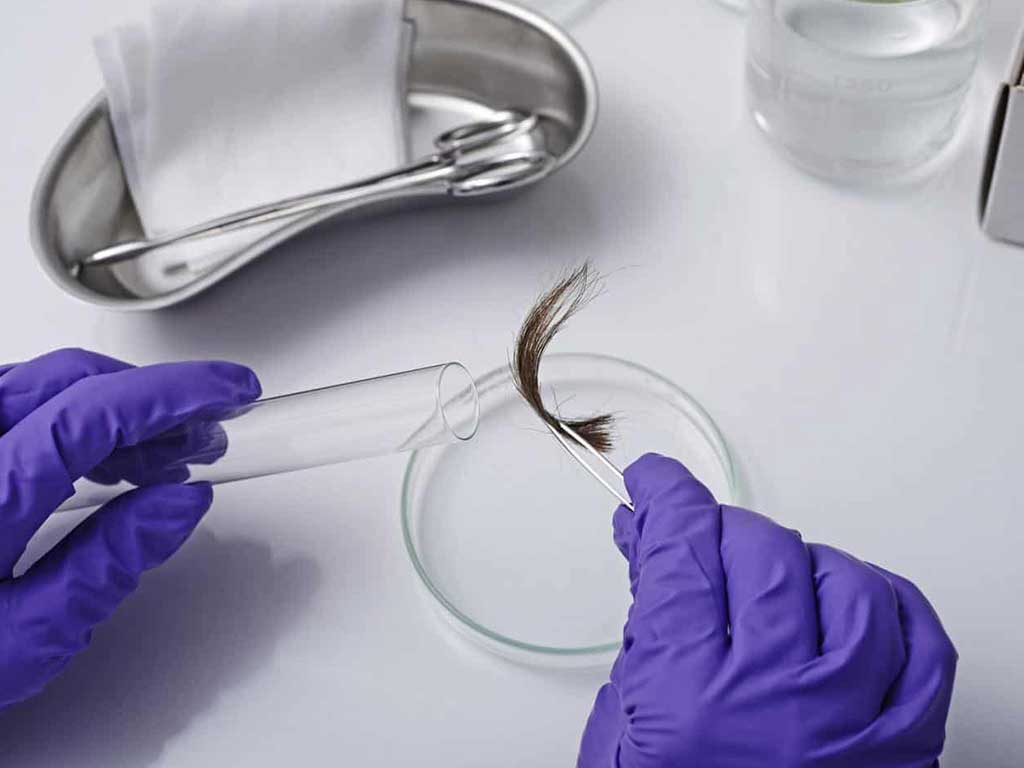
Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Hair Tests
Another type of drug and alcohol test method is hair follicle testing. It involves the collection of a few samples of hair and analysing them for the presence of drugs or alcohol metabolites. Hair tests are unique because they can provide a longer detection window compared to other testing methods. Hair samples can trace substance usage for the past 90 days.
The technology behind hair follicle testing involves Liquid Chromatography-Gas Chromatography (LC-MS) and GC-MS tandem. This process provides greater sensitivity and accuracy. Therefore, it can identify substances that other test methods may miss. However, it also has its limitations, such as needing laboratory equipment to analyse the specimen. It also cannot detect recent substance use, as it takes approximately five to seven days for the metabolites to be incorporated into the hair shaft.
On the other hand, the long detection window of hair offers several advantages. It can be particularly useful in determining long-term or chronic substance use. The test can pinpoint patterns of drug consumption over a longer period. Hence, it is useful in workplace testing programs to identify employees with ongoing drug or alcohol abuse issues.
What Else Can Hair Tests Detect?
Primarily, hair tests can detect the presence of drug and alcohol metabolites. These are compounds or byproducts created after metabolism. Thus, they are indicators of drug use or consumption. The test also establishes certain cut-off levels to determine significant amounts. Additionally, metabolites can stay longer in the system than their parent drugs.
Hair tests can also provide valuable information about the overall health and well-being of a person. For example, hair analysis can determine nutrient deficiencies and hormonal imbalances. It can also help reveal the presence of environmental toxins like lead, mercury, and arsenic, which are critical in certain industries.
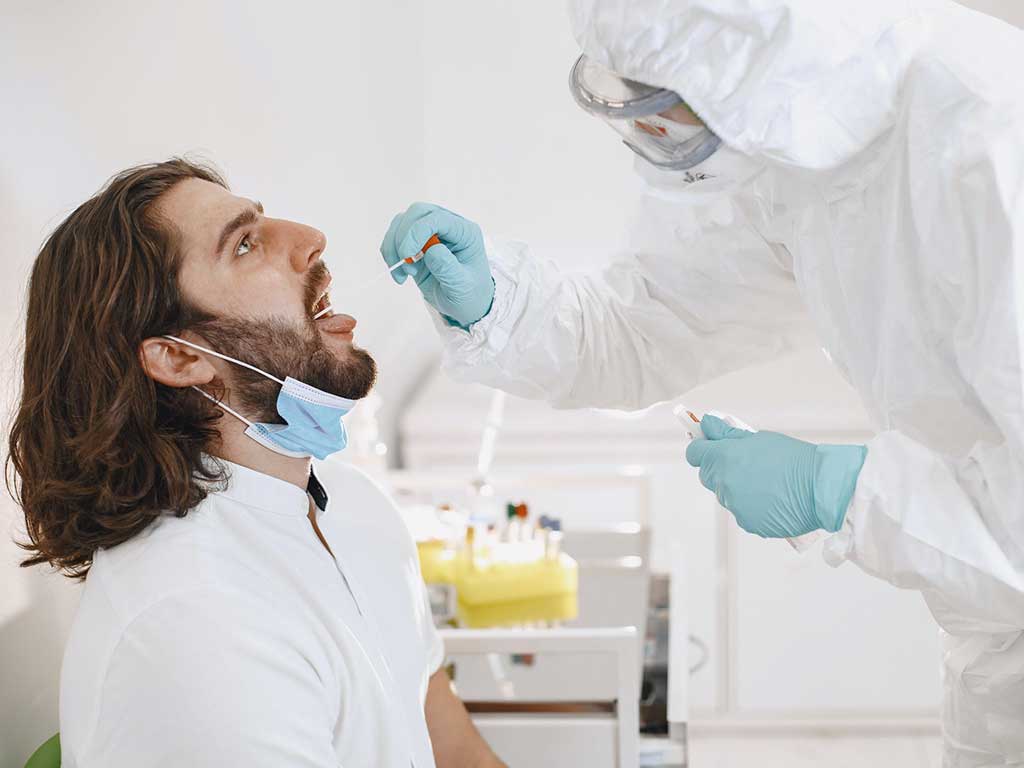

Drug and Alcohol Test Types: Saliva Tests
Saliva screening is a simple process of drug and alcohol tests common in workplaces. This type of test is non-invasive and can provide the results within a few minutes. Additionally, it can detect some substances for up to 48 hours after consumption. Therefore, it is valuable in situations where immediate detection is necessary, such as random drug testing or post-accident testing.
The process of conducting a saliva test is relatively simple. A collector will swab the inside of the mouth and cheek of the person with a pad or sponge. After saturating the collection device with saliva, the collector will place it in a sealed container for analysis. The sample will then be tested using immunoassay techniques to detect any substance.
In some cases, the testing officer will send the sample to a laboratory for further analysis. This is common in situations where the test indicates the presence of drugs or alcohol. In addition, saliva tests can produce accurate results because the test is tamper-resistant.
Advantages of Saliva Tests
- The sample collection process is quick and easy. It eliminates the discomfort of invasiveness often associated with blood or urine tests.
- The sample collection is conducted under direct supervision, minimising the risk of adulteration or tampering.
- Saliva samples have shorter detection windows, determining recent drug use or impairment.
- The test does not require private restrooms or specialised equipment, making it convenient for on-the-spot or on-site screening.
- The results are available within minutes, allowing employers to make informed decisions or necessary interventions.
- Saliva samples can detect common drugs of abuse, including marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, opioids, and benzodiazepines.

Drug and Alcohol Test Methods and Techniques
There are various methodologies and techniques used in drug and alcohol tests. A common type is immunoassay screening. It relies on the binding of antibodies to specific drug metabolites or alcohol markers. This technique is quick and affordable, making it cost-efficient for initial screening. Additionally, they are effective in urine and saliva samples.
Another type is the GC-MS test. It is a highly accurate and sensitive method for quantifying substances. This method involves the separation of drug or alcohol components by gas chromatography, followed by their identification using mass spectrometry. Hence, they are considered the gold standard in alcohol and drug detection or forensic testing.
Furthermore, the LC-MS test is an advanced technique involving the separation, identification, and quantification of substances using the liquid mobile phase. It is particularly useful for complex samples, such as blood and saliva, as it offers high resolution and sensitivity. Some laboratories may combine GC-MS and LC-MS to obtain a more comprehensive analysis. Finally, professional breathalysers employ fuel cells or infrared optical sensors to measure the BAC.
Screening vs Testing
Drug and alcohol screening and testing are often used interchangeably. However, there are some key differences between the two. Drug screening typically refers to the initial step in the process to quickly assess whether a person has consumed drugs recently. This kind of test provides qualitative results.
On the other hand, drug testing is a more comprehensive method of determining substances in the system. It often involves laboratory analysis and using more advanced techniques. In addition, it can give quantifiable results. Due to the complex process involved, lab-based testing takes more time to produce results than rapid screening.

Implementing Drug and Alcohol Tests in NZ
Implementing drug and alcohol tests in NZ workplaces involves several processes and considerations. Firstly, companies should develop a clear and comprehensive drug and alcohol policy. This enables employers to conduct tests under reasonable grounds. The common situations for testing include pre-employment screening, random testing, post-incident testing, and reasonable suspicion testing.
Secondly, employers should consider the types of tests they want to implement. Each test method differs in its levels of accuracy, sensitivity, turnaround time, and ease of use. For example, a hair test may be suitable for pre-employment screening to determine the substance use history of an applicant. It is essential for employees to understand the nature and factors surrounding these tests and their potential implications.
Companies should educate their employees about the testing procedures. This includes informing them about the purpose of the tests, their rights and responsibilities, and consent. Test results should be handled with utmost confidentiality. Finally, costs can impact the frequency of testing. Businesses set a budget as an investment for workplace safety.
Workplace Policy
The workplace policy is a set of rules that guides employers and employees regarding drug and alcohol use. A well-written policy should be clear, concise, and easily understood by all. It typically outlines what constitutes prohibited substances and the testing protocols. For example, it includes the common grounds or reasons for testing.
Moreover, it should specify the consequences of violating the policy, which may include disciplinary action or termination of employment. Equally important, the policy should address employee rights and privacy and other relevant laws. Lastly, any updates should be communicated to all employees and made readily available.

Drug and Alcohol Test Training
Accurate and reliable tests depend on the competence of the individuals administering them. Therefore, it is crucial for those responsible for conducting drug and alcohol tests to undergo proper training. This training should cover the different testing methods, techniques, and equipment used in the process. In New Zealand, individuals who want to become alcohol and drug testers can undergo training through various organisations.
In the first part of the training, participants will learn about the different types of substances and their effects on the body. They will also learn how to recognise the signs of impairment or abuse. Furthermore, the course educates on the legal requirements and standards for testing, sample collection procedures, and chain of custody documentation. Following these protocols help maintain the integrity of the results.
The second part of the training involves practical examinations on the collection and handling of the samples and analysis. Individuals will also learn how to properly communicate the test results with clients, ensuring confidentiality and sensitivity. Lastly, participants should pass both theoretical and practical components of the course to earn their certification.
Australian/New Zealand Standards
- The Australian/New Zealand Standards are a set of guidelines and protocols for alcohol and drug testing in the workplace.
- These standards ensure consistency and accuracy in the testing process, ensuring fair and reliable results.
- Compliance with these guidelines helps organisations meet legal requirements and mitigate potential liabilities related to drug and alcohol use.
- The AS/NZS 4308:2023 is the updated standard for urine drug testing in Australia and New Zealand.
- AS/NZS 4760:2019 sets the standards for oral fluid testing.
- The AS 3547:2019 ensures quality assurance in breathalyser testing. This certification meets the requirements of breath screening devices.
Conclusion
Drug and alcohol tests are valuable tools in detecting impairment and substance abuse in the workplace. This measure helps minimise safety risks, such as accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Consequently, organisations can protect the well-being of their employees and maintain productivity in the long run. These tests utilise various methods, including urine, saliva, breath, hair, and blood analysis. It can detect a wide range of substances, such as illegal drugs, abused prescription medications, and alcohol.
An effective workplace testing program includes establishing comprehensive policies. The policy outlines the safety procedures, prohibited substances, reasons for testing, and the consequences of violations. The consequences of positive drug results may include disciplinary actions and even termination. Therefore, the accuracy of the test is crucial to prevent legal challenges. Fortunately, the AS/NZS Standards provide organisations with a set of guidelines to ensure the reliability and integrity of the procedures.