Mandatory Drug and Alcohol Testing: What It Is & the Methods of Testing
01 March, 2024

With the rise of substance abuse issues in society, mandatory drug and alcohol testing has become crucial to ensure a safe work environment. It is the practice of requiring individuals to undergo a substance use test. There are several methods available to trace the presence of ethanol or illegal drugs in the system. This includes breath, urine, saliva, blood, and hair tests. These can identify several substances that can cause impairment to the physical and cognitive abilities of individuals.
Substance abuse can severely impact the life of an individual. It can also negatively affect those around them and their community. Hence, companies implement testing policies to maintain a safe working environment. The policies also allow them to comply with their legal employer obligations and outline the expected behaviours of employees. This article will present information on mandatory alcohol and drug tests, the types of methods, and legalities.
What is Mandatory Drug and Alcohol Testing?
Mandatory drug and alcohol testing refers to the practice of requiring individuals to undergo alcohol and drug testing. It is done to check for the presence of drugs and ethanol in the system. Due to the prevalence of substance use disorders, it has become more common and important in various industries.
Many organisations, including workplaces, government agencies, and healthcare institutions, implement mandatory testing. Employers typically require testing for employees in safety-sensitive positions. Meanwhile, law enforcement officers use them to identify individuals who pose safety risks by committing drink or drug driving offences. Lastly, healthcare professionals conduct tests to monitor the recovery of patients in rehabilitation programs.
Screenings are necessary to ensure the health and safety of individuals. Moreover, it prevents the negative impacts of drug and alcohol abuse from impacting the community as a whole. Alcohol and drug addiction can cause severe health issues, like kidney and liver diseases. They also increase the likelihood of accidents due to impairments like loss of coordination, slow reaction times, and vision problems.
Importance of Mandatory Testing
- Mandatory testing deters individuals from illicit drug and alcohol use.
- It helps identify individuals who are breaking the legal limits and committing criminal offences by driving under the influence of drugs and alcohol. It can also provide evidence after car crashes or other accidents.
- Testing helps employers objectively recognise which employees have broken the workplace drug and alcohol policy and enforce the appropriate disciplinary action.
- It helps employers comply with legislation in relation to their obligation to maintain a productive and safe workplace.
- Testing can facilitate interventions for people with substance abuse issues and help them get resources for drug or alcohol treatment.
Types of Methods for Mandatory Drug and Alcohol Testing
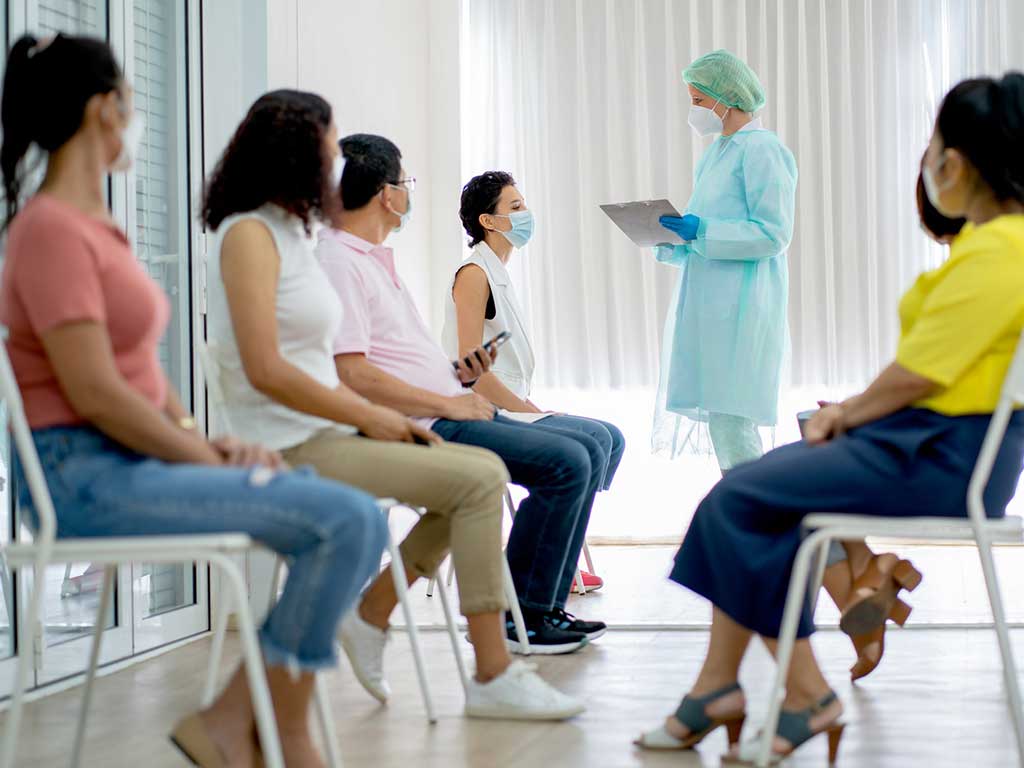
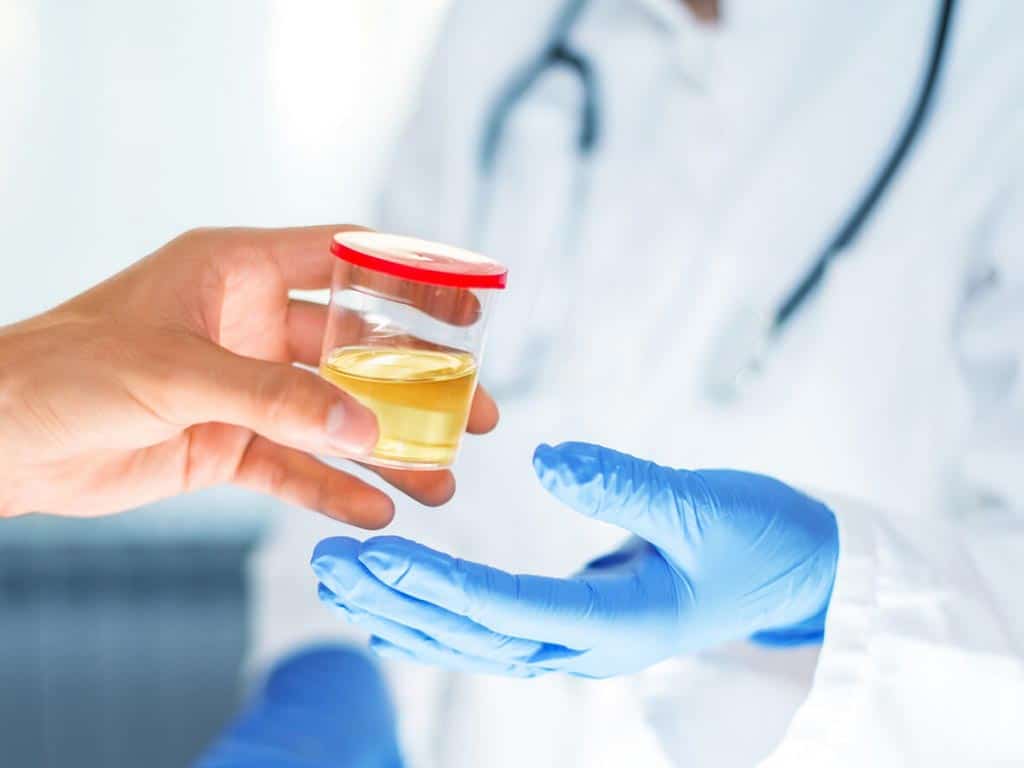
There are several alcohol and drug testing methods that organisations can use. For mandatory drug and alcohol testing in workplaces, urine screening is the standard method for testing for drugs and alcohol. It uses urine samples to detect a wide variety of substances for days to weeks, depending on the substance.
Saliva testing is a convenient method of testing for the misuse of alcohol, prescription drugs, and illegal substances. It is common for onsite testing due to its easy collection procedure. Moreover, its short detection period is ideal for tracing recent use. Another convenient method for alcohol screening is breath testing. This typically uses a breathalyser to measure the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) levels.
Blood testing is another option for identifying substance abuse. It is considered the most accurate method. However, it is less common for screenings because of its invasive collection procedure. Lastly, hair follicle testing is helpful for the substance use history of an individual. It helps businesses during pre-employment screenings. It can also be used for legal proceedings.
Detectable Substances
A wide variety of substances can be detected using blood, hair, urine, and saliva tests. However, this depends on what panels are used during analysis. Some commonly detected substances are amphetamines, ethanol, heroin, morphine, benzodiazepines, cannabis, and cocaine. Testing may also trace barbiturates, oxycodone, methadone, and phencyclidine.
Alcohol and drug test kits can have 5 to 12 panels for quickly testing individuals. Meanwhile, laboratories can use more panels and account for cross-reactivity for more accurate results. However, it is essential to note that the price also increases depending on the amount of substances they wish to test for.

Legalities of Mandatory Drug and Alcohol Testing
Mandatory drug and alcohol testing is a common practice, especially for businesses in high-risk industries like construction, mining, and transportation. While it is legal for employers to conduct tests, they must still ensure compliance with relevant legislation and regulations and respect the rights of their employees.
Companies should have a clear drug and alcohol policy that outlines the testing procedures, the consequences of a non-negative or positive result, and expected behaviours from employees. It should also address key issues while informing workers of their rights related to the alcohol and drug testing process. Some employers consult legal professionals for advice regarding their policies.
Moreover, companies must protect the privacy of their workers by creating confidentiality measures. Only relevant staff should have access to medical information and test results. Furthermore, it can help to include a complaints process for those who wish to refute the drug screening report. Overall, employers must adhere to legal guidelines when conducting mandatory testing policies for successful results.
Implications of a Non-Negative Result
A non-negative result from an alcohol and drug screening indicates that trace amounts of a substance exceeding the cut-off level were found in the sample. This means the individual has potentially broken the workplace policy and should face disciplinary action. However, some may petition for a confirmatory test if they believe this is a false-positive result.
Compared to initial screening, laboratory confirmatory tests use advanced analysis methods. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) is the gold standard for it. This is because it can accurately quantify the substances. The confirmation test results can trump the initial report if it produces a negative report.
Conclusion
Mandatory drug and alcohol testing is essential for companies in high-risk industries to maintain workplace health and safety. It helps reduce accidents that can cause injuries or fatalities. Moreover, there are several methods that organisations can use for comprehensive tests. Breath testing provides quick measurements of the BAC to identify alcohol intoxication. Meanwhile, saliva and urine testing are convenient and cost-effective ways to test for a variety of substances, like amphetamines, cocaine, cannabis, and heroin.
However, employers must still comply with the relevant safety legislation and regulations when conducting these tests. This is why they form policies and consult legal professionals before implementing them. They must protect the rights of their employees by ensuring their medical information, including test results, remains confidential. They should also use reliable drug and alcohol test kits or devices to ensure accurate results. Some workplace testing kits and devices are available here at Breathalysers New Zealand.