Non DOT Drug Test Alcohol: What It Is & the Testing Methods Used
18 April, 2024

Non-DOT drug test for alcohol is a procedure independent of the regulations set forth by the Department of Transportation (DOT). Private employers often utilise this form of testing as part of their internal policies to ensure workplace safety and productivity. Additionally, it may extend to broader safety concerns, including road safety. There are various methods to perform non-DOT alcohol testing. These include urine, saliva, blood, hair, and breath tests.
Alcohol use in the workplace can lead to a multitude of problems, ranging from decreased productivity to serious safety hazards. Employees under the influence of alcohol are more prone to making errors, poor decision-making, and accidents. Moreover, alcohol-related incidents can tarnish reputation and result in legal liabilities. Thus, implementing non-DOT alcohol tests becomes crucial for employers to identify and address alcohol misuse proactively. This article will present non-DOT alcohol testing, including its methods and steps for conducting one.
What is a Non-DOT Drug Test for Alcohol?
A Non-DOT drug test for alcohol is a type of alcohol screening that is outside the regulations of the DOT. Generally, DOT regulations govern safety-sensitive duties, and they mandate specific testing protocols for alcohol and drug screening. On the other hand, non-DOT testing is typically implemented by private companies or business owners. It varies in terms of protocols, procedures, and cutoff levels for alcohol detection.
In workplaces where safety issues are a concern, implementing alcohol testing programs is a common practice. This involves conducting random testing or including alcohol screening as part of pre-employment testing for new hires. Additionally, employers may also conduct alcohol tests on current employees if there are suspicions of substance abuse or if safety incidents occur on the job.
Employers who conduct non-DOT tests still need to follow the law. They should ensure their testing policies are fair and accurate and respect the privacy rights of their employees. This means they should use methods that do not discriminate, provide reliable results, and keep employee information confidential. Hence, following these standards helps maintain trust between employers and employees while upholding legal and ethical principles.
Non-DOT vs. DOT Test
Non-DOT Test:
- Employers not regulated by DOT use this test.
- They typically conduct it in regular workplace settings.
- The results mainly impact employment within the company.
- They usually have more flexibility in testing procedures and requirements.
- Companies may choose not to report results externally unless they are legally required or as per company policy.
DOT Test:
- Employees in safety-sensitive positions under DOT regulations must take this test.
- DOT mandates strict procedures for conducting it.
- The results can affect the ability of the person to work in safety-sensitive roles across different companies.
- DOT regulations specify the procedures and cutoff levels.

Methods for Non-DOT Drug Tests for Alcohol
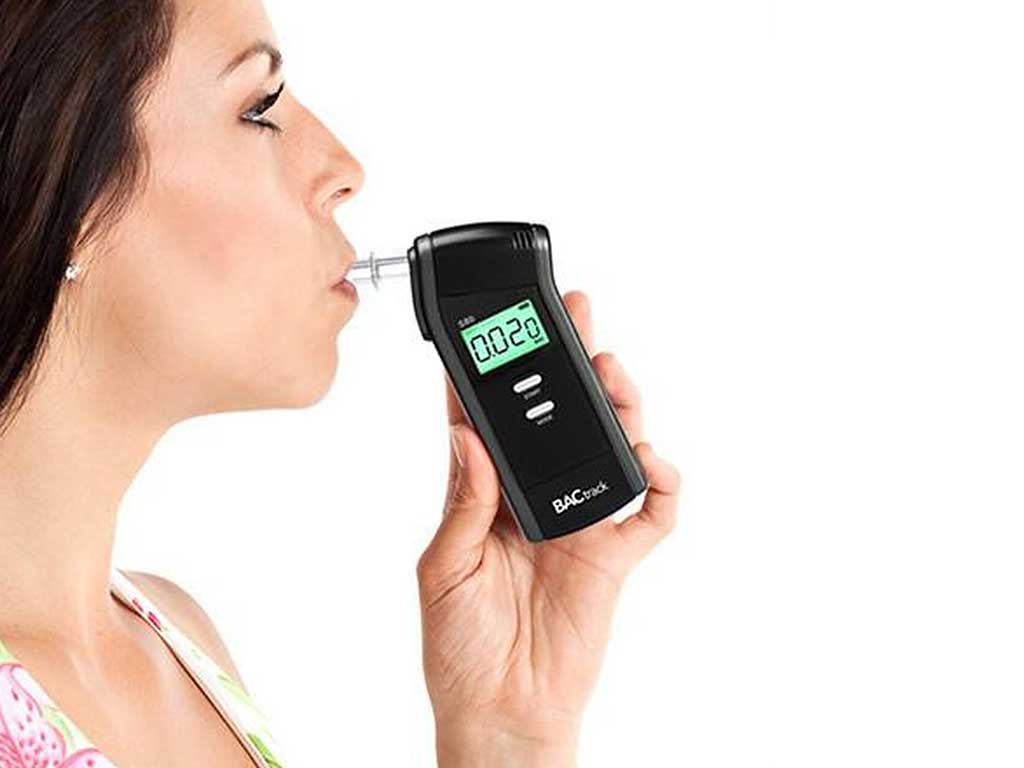
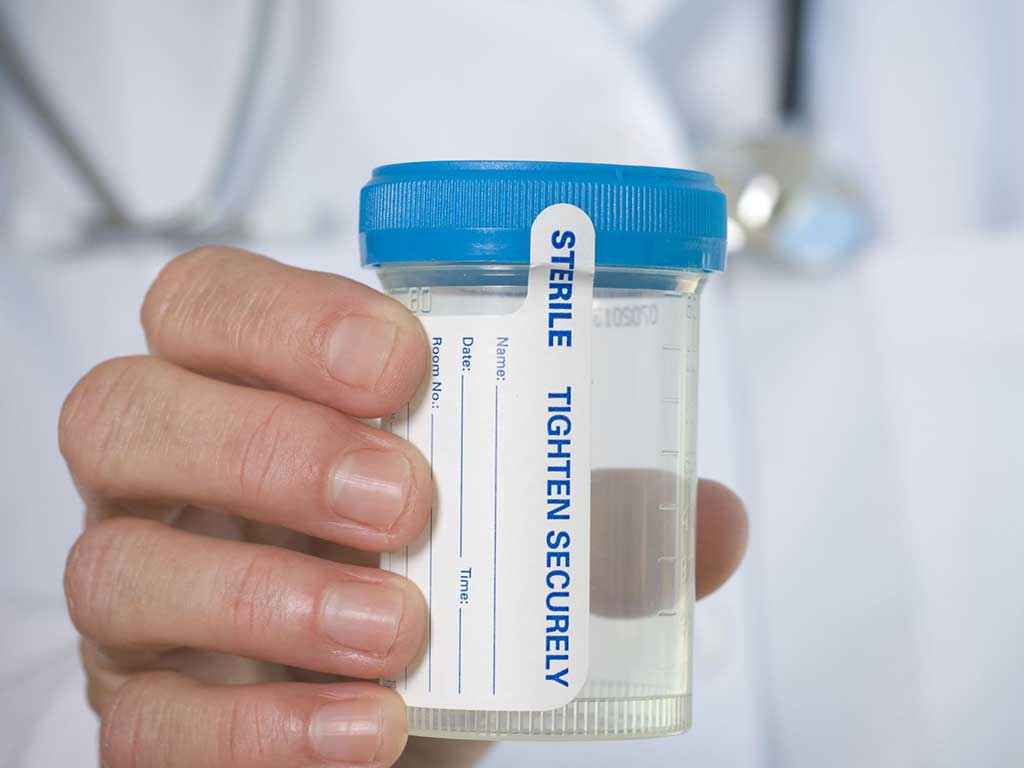
When it comes to non-DOT drug tests for alcohol, there are various methods to detect its presence. Firstly, urine test. A person provides a urine specimen, usually in a collection container, which is then analysed for alcohol content. Secondly, saliva testing involves swabbing the inside of the cheeks to collect saliva samples. This method is quick and non-invasive.
Thirdly, blood testing. It involves taking blood samples to determine alcohol levels. This method is highly accurate and can provide precise results. However, it is more invasive and requires skilled personnel for sample collection. Fourthly, a hair follicle test is a method that analyses scalp or body hair for traces of alcohol. This approach has a longer detection window compared to other methods.
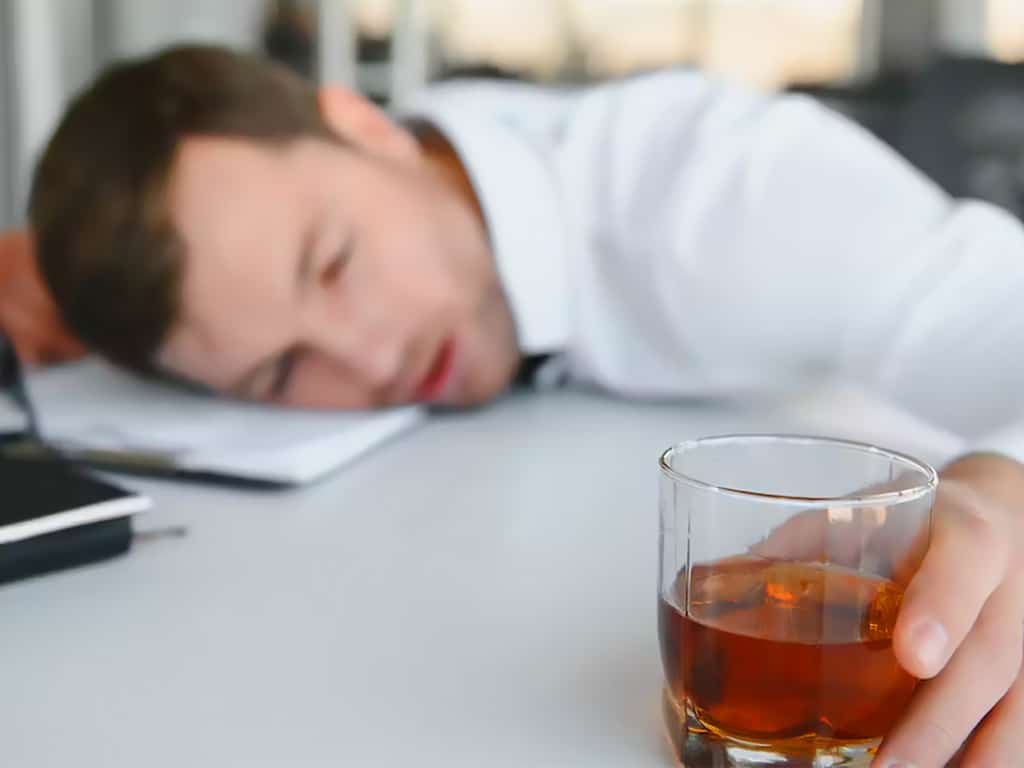
Lastly, breath alcohol testing measures the alcohol content in the breath sample. It provides immediate results and is relatively non-invasive. Non-DOT employers often use workplace breathalysers to quickly screen employees for alcohol use before or during work shifts. Overall, the choice of method usually depends on factors such as the required detection window, ease of sample collection, and the need for immediate results.
What is the Most Common Testing Method?
The breath test is the most common alcohol testing method. It works by measuring the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) in the breath using a breathalyser. This method is popular because it is non-invasive, quick, and relatively accurate. Law enforcement officers or employers can administer breath tests on the spot.
However, properly using a breathalyser is vital in ensuring valid and accurate BAC tests. For instance, it is necessary to wait 15 to 20 minutes after eating, smoking, or drinking before taking a breath test. The waiting period gives the body enough time to process alcohol and reach the lungs.
Steps Involved in Conducting a Non-DOT Drug Test for Alcohol
The first step in conducting a non-DOT drug test for alcohol is the collection of biological samples. This involves obtaining bodily fluids or tissues from the individual. The testing officer collects specimens safely and hygienically to ensure accuracy and maintain the integrity of the testing process.
In the analysis stage, laboratories employ methods such as Immunoassay and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) to detect substances accurately. Immunoassay quickly screens samples for alcohol metabolites. If a positive result occurs, the sample undergoes confirmatory testing using GC-MS, a highly precise method of identifying specific substances. This rigorous testing regime minimises the risk of false positives, ensuring reliable results aligned with relevant standards.
Upon completion, professionals generate a report for interpreting results. They analyse the findings, considering factors such as drug concentrations and cutoff levels. This analysis provides a comprehensive assessment. It aids in identifying alcohol use. However, refusing to take a test may result in penalties, demotion, grounds for transfer and termination. Therefore, individuals must comply with testing procedures and cooperate throughout the process.
Understanding the Results
Understanding alcohol testing results is essential for various reasons. It helps determine if someone is under the influence of alcohol, which can affect their judgment and ability to perform tasks safely. A positive test result indicates impairment and poses a risk to themselves and others in the workplace.
On the other hand, a negative result indicates no presence of alcohol in the system. However, factors such as individual tolerance, medical conditions, and timing of alcohol consumption can affect the test outcomes. Therefore, confirmatory testing and professional interpretation are essential to rule out false positives or negatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, non-DOT drug tests for alcohol are vital tools for ensuring workplace safety and regulation compliance. Employers utilise various methods like urine, saliva, blood, hair follicle, and breath tests to detect alcohol presence. These tests are crucial for pre-employment screenings, random testing, and addressing suspicions of substance abuse among employees. Adhering to fair, accurate, and confidential testing practices fosters trust between employers and employees while upholding legal and ethical standards.
Conducting a non-DOT alcohol test involves several crucial steps to ensure accuracy and reliability. Collection of biological samples is the initial stage, followed by analysis like Immunoassay and GC-MS to detect alcohol metabolites. The interpretation of results is vital, considering factors such as drug concentrations and cutoff levels. Understanding test outcomes helps identify impairment and ensures workplace safety. Compliance with testing procedures is essential, as refusal may lead to disciplinary actions.